Wednesday, March 10, 2010
Ultra simple incremental backups with rsync
Then I found this webpage that provides some scripts to achieve circular snapshots.
However, most scripts on the web are extremely large and complex compared to what I need. So finally I made my own script that makes automated incremental backups, with no cycling but keeping a history file to identify each backup.
Here is the code:
This script will create backup directories called backup.xxxx, where xxxx is the backup number. This number is zero for the first backup done. Rsync hard-links the unchanged files to the previous backup which is a key method to save space.
With this script I am backuping a NTFS partition and that's why the option --modify-window=1 is needed in rsyncFlags. It is important to write sourceDir without a trailing forward slash!
In order to provide easy access to the last backup, a symbolic link called HEAD will point to the latest backup. Additionally, a file called backup-history holds the exact time and date where each backup was performed.
NOTE: I am not responsible for this script and it's correctness. There might be problems such as if there are backup.something folders or files in the backup directory where the script is called, and other bugs that may arise. This is a very simple and minimalistic script!
Monday, March 1, 2010
Merging Qt and Eigen
#ifndef MIMG_H
#define MIMG_H
USING_PART_OF_NAMESPACE_EIGEN
#include <QImage>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Array>
//general type, maybe float or double needed
typedef MatrixXf MImgType;
class MImg
{
public:
//creates an all-black image
MImg(unsigned int h, unsigned int w);
//creates image from QImage
MImg( const QImage &img );
MImgType R,G,B; //each component
//made public for faster access
unsigned int getHeight();
unsigned int getWidth();
QImage * toQImage(); //convert to QImage
/**
Maximizes dynamic range of three channels
independently!
**/
void maximizeIndependentDynamicRange();
private:
unsigned int mH,mW; //height, width
};
#endif // MIMG_H
#include "mimg.h"
MImg::MImg(unsigned int h, unsigned int w)
{
R = MImgType::Zero(h,w);
G = MImgType::Zero(h,w);
B = MImgType::Zero(h,w);
mH = h;
mW = w;
}
MImg::MImg( const QImage &img )
{
int w = img.width();
int h = img.height();
R = MImgType::Zero(h,w);
G = MImgType::Zero(h,w);
B = MImgType::Zero(h,w);
//now copy values..
for (int y=0; y < h; y++)
for (int x=0; x < w; x++)
{
QRgb color = img.pixel(x,y);
R(y,x) = qRed(color)/255.0;
G(y,x) = qGreen(color)/255.0;
B(y,x) = qBlue(color)/255.0;
}
return img;
}
void MImg::maximizeIndependentDynamicRange()
{
double min, max;
min = R.minCoeff(); max = R.maxCoeff();
R = (R.cwise() - min) / (max - min);
min = G.minCoeff(); max = G.maxCoeff();
G = (G.cwise() - min) / (max - min);
min = B.minCoeff(); max = B.maxCoeff();
B = (B.cwise() - min) / (max - min);
}
unsigned int MImg::getHeight() {
return mH;
}
unsigned int MImg::getWidth() {
return mW;
}
Thursday, December 3, 2009
Matlab and n-dimensional array sorting
- A=[1 2; 6 5]; B = reshape(A,[1 4]);
- [sV, sI] = sort(B, 'descend'); % sort linearised array
- disp(sV(1)); %show max value: 6
- disp(sI(1)); %show max index: 2
- [x,y] = ind2sub( size(A), sI(1) );
- disp(x); disp(y); % (x,y) == (2,1), we got the coordinates in the original matrix
Saturday, August 15, 2009
FPGAs are taking over!
Saturday, July 4, 2009
Qt-Embedded: Capturing screen with QPixmap
mainWindow::mainWindow()
{
// captureTimer should be declared in mainWindow's class definition
captureTimer = new QTimer(this);
connect( captureTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()), this, SLOT(captureTimerEvent()) );
captureTimer->start(1000); //check interval
}
void mainWindow::captureTimerEvent()
{
QString tmpFile = QString("/tmp/doCapture");
if ( !QFile::exists(tmpFile) )
return;
QFile f(tmpFile);
if ( !f.open( QIODevice::ReadWrite ) )
return;
char buf[200];
if ( f.readLine( buf, sizeof(buf) - 4 ) == -1 )
return;
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0'; //remove \n created by 'echo'-- not safe!
strcat( buf, ".png" );
//capture
QPixmap p = QPixmap::grabWindow( this->winId() );
if ( p.save( buf ) )
printf("------- GRAB OK\n");
else
printf("------- ERR GRAB!\n");
/* delete file */
f.remove();
}
echo pngfilename > /tmp/doCapture
Monday, May 4, 2009
Compiling and using GDB for arm-linux
Some days ago I had to compile gdb manually in order to debug an arm-linux app. It's quite trivial but it's so useful that I thought it would be a nice idea to post the instructions here. Below there are some explanations about debugging remotely with KDevelop.
This was done with gdb-6.8, you can grab it here. It is assumed that arm-linux tools are available (PATH correctly set).
Compiling the GDB client
Decompress gdb-6.8 and compile it by issuing:
tar xvf gdb-6.8.tar.gz
cd gdb-6.8
./configure --build=x86 --host=x86 --target=arm-linux
make
After compiling just copy gdb/gdb to arm-linux-gdb where the arm-linux toolchain binaries reside (this is purely for organization and proper naming). You can now remove the gdb-6.8 directory.
NOTE: if your host computer architecture isn't intel-based just replace x86 by the correct value for your platform.
Compiling the GDB server (ARM)
Decompress gdb-6.8 and compile it by issuing:
tar xvf gdb-6.8.tar.gz
cd gdb-6.8
./configure --host=arm-linux
make
After compiling just copy gdb/gdbserver/gdbserver to your arm-linux filesystem so that you can execute it from a remote shell (gdbserver will be an arm-elf binary). You can now remove the gdb-6.8 directory.
Testing connections
First the server should be started in the arm processor by issuing something like:
gdbserver host:1234 _executable_
Where _executable_ is the application that is going to be debugged and host:1234 tells gdbserver to listen for connections to port 1234.
To run gdb just type this in a PC shell:
arm-linux-gdb --se=_executable_
After that you'll get the gdb prompt. To connect to the target type:
target remote target_ip:1234
To resume execution type 'continue'. You can get an overview on gdb usage here.
Debugging with KDevelop
KDevelop can be used to watch variables and debug the remote target (place breakpoints, stop execution, etc). Just go to Project -> Project Options and make sure you have something like this:
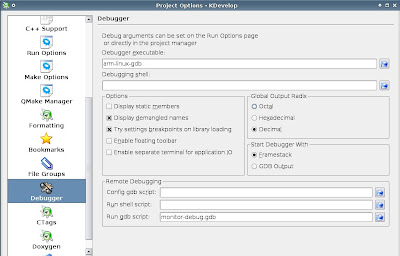
monitor-debug.gdb is a file that contains the following
target remote target_ip:1234
After this you will be ready to remotely debug any arm-linux application.
_
Tuesday, April 28, 2009
Catching uncaught exceptions in Java
package bodyguard;
public class BodyGuard implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler
{
static private BodyGuard bGuard;
static public void registerGuard() {
bGuard = new BodyGuard();
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(bGuard);
}
public void uncaughtException( Thread thread, Throwable e )
{
java.io.StringWriter sW = new java.io.StringWriter();
e.printStackTrace( new java.io.PrintWriter(sW));
String s = "A fatal error was detected during execution: \n" +
"Thread: " + thread.getName() + "\n" +
"Exception: " + sW.toString() + "\n" +
"The application will be closed now.";
showFatalErr(s);
}
private void showFatalErr( String err )
{
//JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, err,"Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
BodyGuardDialog dlg = new BodyGuardDialog(null, true, err);
dlg.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
dlg.setVisible(true);
System.exit(-1); //exit n ow
}
}

